HashMap源码解析
HashMap源码解析
作为面试必问的hashmap,我们今天来一起来探究一下他的源码。这里先贴一张 hashmap 的内部类和部分方法函数
一、什么是 哈希, 哈希函数(散列函数)
Hash,一般翻译做散列、杂凑,或音译为哈希,是把任意长度的输入(又叫做预映射pre-image)通过散列算法变换成固定长度的输出,该输出就是散列值。这种转换是一种压缩映射,也就是,散列值的空间通常远小于输入的空间,不同的输入可能会散列成相同的输出,所以不可能从散列值来确定唯一的输入值。简单的说就是一种将任意长度的消息压缩到某一固定长度的消息摘要的函数。
上面是百度百科的解释。我们可以简单的概括为
- hash 就是将 任意的输入 通过 一种 特殊的算法 变成 长度固定 的输出。
- 可以类似于一种摘要算法,获取我们输入内容的特征来生成一个简短的摘要
- 由于算法可以保证:相同的输入每次都是可以得到相同的输出,即hash值
- 但是也会发生:不同的输入哈希之后会得到相同的结果 即 哈希冲突
object 中的 hashcode 方法
1 | public native int hashCode(); |
方法本身是 native 方法,调用了底层的的类库,根据注释:
hashCode 遵守着如下的约定:
- Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during an execution of a Java application, the hashCode method must consistently return the same integer, provided no information used in equals comparisons on the object is modified. This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an application to another execution of the same application.
- If two objects are equal according to the equals(Object) method, then calling the hashCode method on each of the two objects must produce the same integer result.
- It is not required that if two objects are unequal according to the equals(Object) method, then calling the hashCode method on each of the two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.
翻译一下就是
在程序一次执行的过程中,无论何时被调用,这个方法都会返回相同的值。但是程序的多次执行就不能保证每一次都相等
如果两个对象的 equals 方法返回 true,那么他们调用此方法就一定返回相同的结果
当然也不一定要确保:两个对象如果根据重写的 equals 方法返回为 false,那么此方法的返回结果一定不同。
即:两个对象 根据重写的equals判断为不相等,此时的 hashcode 也可以相同
不过我们在写程序时应该注意尽量是不同的对象返回不同的hashcode,以便加强哈希效率,避免哈希冲突
hashmap 采用的哈希方法
1 | static final int hash(Object key) { |
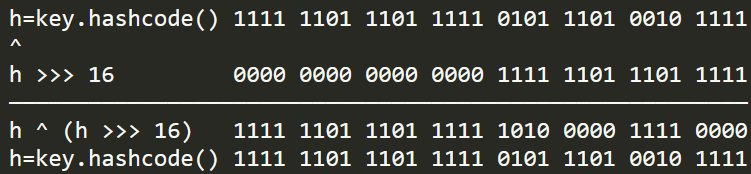
将h无符号右移16为相当于将高区16位移动到了低区的16位,再与原hashcode做异或运算,可以将高低位二进制特征混合起来。即哈希扰动。
从上文可知高区的16位与原hashcode相比没有发生变化,低区的16位发生了变化。
我们都知道重新计算出的新哈希值在后面将会参与hashmap中数组槽位的计算,计算公式:(n - 1) & hash,假如这时数组槽位有16个,则槽位计算如下:
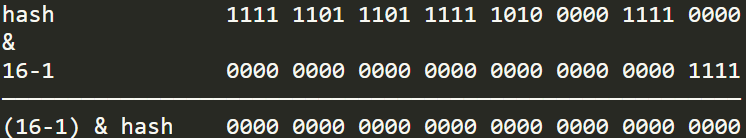
高区的16位很有可能会被数组槽位数的二进制码屏蔽,如果我们不做刚才移位异或运算,那么在计算槽位时将丢失高区特征
也许你可能会说,即使丢失了高区特征不同hashcode也可以计算出不同的槽位来,但是细想当两个哈希码很接近时,那么这高区的一点点差异就可能导致一次哈希碰撞,所以这也是将性能做到极致的一种体现
取余 % 和位运算 &
我们看到源码中存放值的时候:(n - 1) & hash
一般来说我们的认为都是将 哈希值 和数组的长度进行取模运算来获得数组的下标
- 那么这里主要考虑到的是:位运算相比取模运算效率更高
关于为什么位运算能代替取模运算可以参考这个 👉由HashMap哈希算法引出的求余%和与运算&转换问题
当 lenth = 2n 时,X % length = X & (length - 1)
- 也就是说,长度为2的n次幂时,模运算 % 可以变换为按位与 & 运算。
比如:9 % 4 = 1,9的二进制是 1001 ,4-1 = 3,3的二进制是 0011。 9 & 3 = 1001 & 0011 = 0001 = 1
再比如:12 % 8 = 4,12的二进制是 1100,8-1 = 7,7的二进制是 0111。12 & 7 = 1100 & 0111 = 0100 = 4
- 上面两个例子4和8都是2的n次幂,结论是成立的,那么当长度不为2的n次幂呢?
比如:9 % 5 = 4,9的二进制是 1001,5-1 = 4,4的二进制是0100。9 & 4 = 1001 & 0100 = 0000 = 0。显然是不成立的。
二、存储方式和数据结构
问:HashMap的底层数据结构是什么
答:数组+链表+红黑树
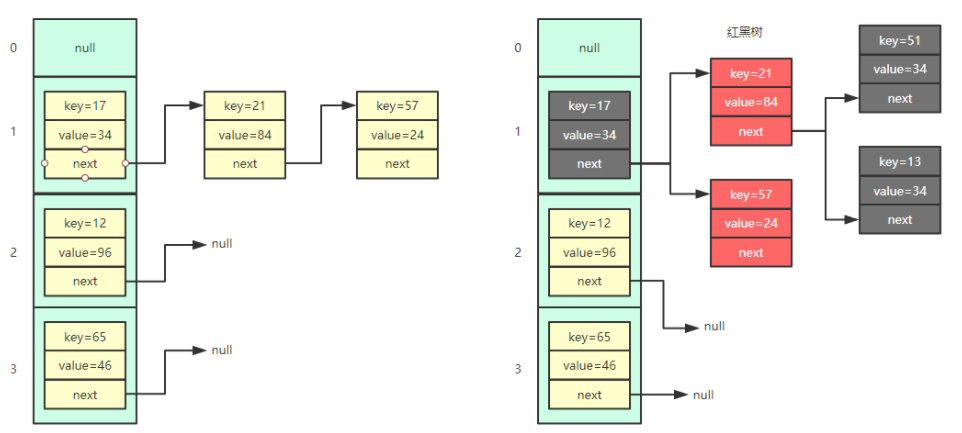
从上面的图中我们可以看出hashmap的存储结构,默认是数组+链表的结构。
当链表的长度大于 8 (默认) 的时候,链表会转换为红黑树。
node 的数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;node 结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
/**
* node结点的哈希值:将 key 的哈希值和 value 的哈希值进行异或运算
*/
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}treenode 结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/**
* Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
* linked node.
*/
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
}
Hashmap中的链表大小超过八个时会自动转化为红黑树,当删除小于六时重新变为链表
三、构造方法和初始化
1 | /** |
这个是最后被调用的构造方法,本质上就是先给 hashmap 初始两个值:initialCapacity 和 loadFactor:即初始容量和负载因子
1. 初始容量 initialCapacity
1 | /** |
这里我们以输入 9 为例
n = cap - 1;
这里如果直接没有 -1 操作,如果输入的为2的幂,补1之后再+1,就不会返回原值而是 cap*2
n = 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
n |= n >>> 1
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000 n
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000100 n >>> 1
======================================
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001100 => n
n |= n >>> 2
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001101 n
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011 n >>> 2
======================================
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001111 => n
后续操作使得后续全为一
最后检查 大于零且小于最大值,将结果加一返回:16
2. 负载因子 loadFactor
1 | /** |
这个值和我们hashmap的扩容有关:比如说当前的容器容量是16,负载因子是0.75,16*0.75=12,也就是说,当容量达到了12的时候就会进行扩容操作
此处我们可以从时间和空间的角度来考虑:
- 当负载因子的值为 1
- 此时只有当 node 数组被填满时才会进行扩容
- 既然哈希碰撞是不可避免的,那么此时底层的红黑树结构就会变得异常复杂,明显会降低查询效率
- 时间换空间
- 当负载因子的值为 0.5
- 此时当 node 数组被填充超过一半就会进行扩容
- 那么虽然可以降低底层红黑树的结构提高查找效率,也无疑牺牲了一半的存储空间
- 空间换时间
所以 0.75 的选择可以说是空间和时间的权衡。但最后的 0.75 也并不是简单的 0.5 和 1 的折中。
根据源码的注释,里面涉及到一些统计学方面的泊松分布的计算,这里就不展开细说了。
1 | /** |
四、添加元素和查找元素
1. put 方法
1 | /** |
这里贴一张流程图并且附上加了注释的源码
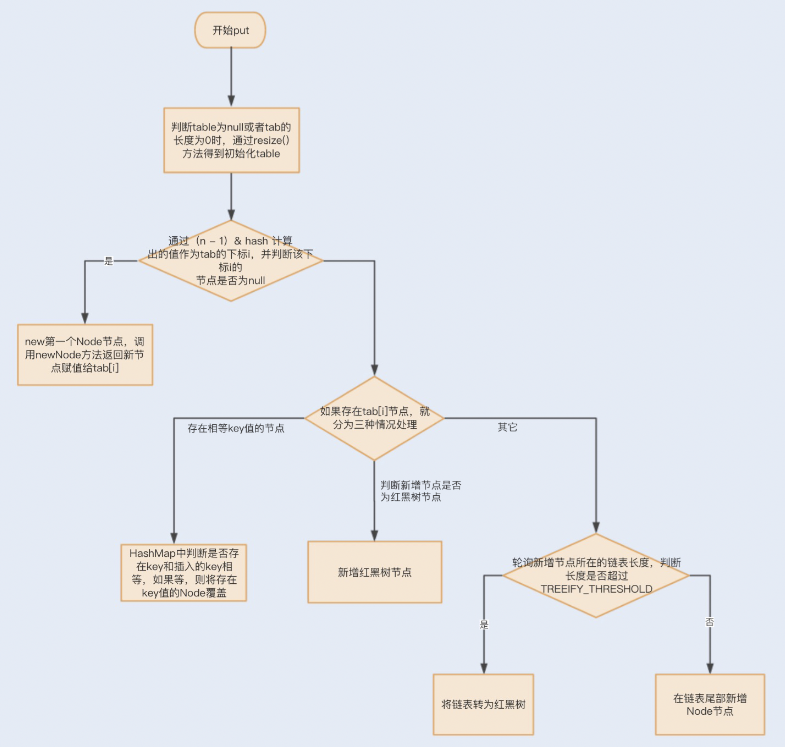
1 | /** |
2. get 方法 和 containsKey 方法
1 | public V get(Object key) { |
1 | public boolean containsKey(Object key) { |
这里我们可以看到底层都是调用了
getNode()这个方法通过哈希值和键值去搜索结点
containsKey:如果找到结点则返回 true,否则返回 false
get:如果找到结点返回结点的 value 值,否则返回 null
- 不过要注意的是,这里如果返回了 null 可能有两种原因:
- key 不存在
- key 存在,但是存储的结果为 null
1 | final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { |
五、扩容和rehash
这里我们先上resize()函数的源码
1 | final Node<K,V>[] resize() { |
这个函数一般提供两个功能:
- 在构造函数之后,第一次
put()发现数组为空则会调用,实现懒加载 - 当存储的数据超过阈值时调用,来实现扩容
经过rehash之后,元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动2次幂的位置


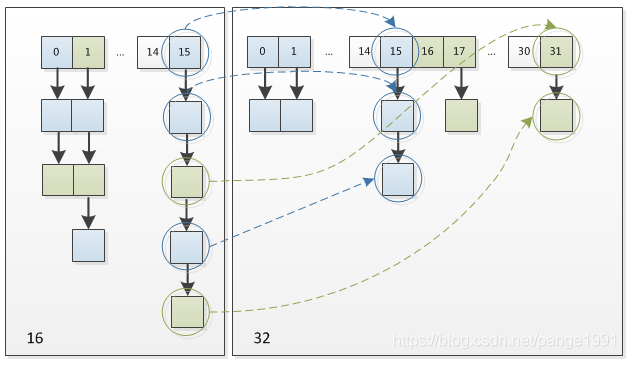
扩容是一个特别耗性能的操作,所以当程序员在使用HashMap的时候,估算map的大小,初始化的时候给一个大致的数值,避免map进行频繁的扩容。
负载因子是可以修改的,也可以大于1,但是建议不要轻易修改,除非情况非常特殊。
六、头插法和尾插法
JDK8以前是头插法,JDK8后是尾插法
头插法和尾插法,顾名思义就是插入链表的时候插入在链表头部还是尾部。
由于HashMap在扩容时采用头插法会造成链表死循环,故在JDK8之后调整为尾插法。
这里贴一个别人的分析
- 前提条件:
- hash算法为简单的用key mod链表的大小。
- 最开始hash表size=2,key=3,7,5,则都在table[1]中。
- 然后进行resize,使size变成4。
- 未resize前的数据结构如下:
如果在单线程环境下,最后的结果如下:
这里的转移过程,不再进行详述,只要理解transfer函数在做什么,其转移过程以及如何对链表进行反转应该不难。
然后在多线程环境下,假设有两个线程A和B都在进行put操作。线程A在执行到transfer函数中第11行代码处挂起,因为该函数在这里分析的地位非常重要,因此再次贴出来。
此时线程A中运行结果如下:
线程A挂起后,此时线程B正常执行,并完成resize操作,结果如下:
这里需要特别注意的点:由于线程B已经执行完毕,根据Java内存模型,现在newTable和table中的Entry都是主存中最新值:7.next=3,3.next=null。
此时切换到线程A上,在线程A挂起时内存中值如下:e=3,next=7,newTable[3]=null,代码执行过程如下:
1 | newTable[3]=e ----> newTable[3]=3 |
此时结果如下:
继续循环:
1 | e=7 |
结果如下:
再次进行循环:
1 | e=3 |
注意此次循环:e.next=7,而在上次循环中7.next=3,出现环形链表,并且此时e=null循环结束。
结果如下:
在后续操作中只要涉及轮询hashmap的数据结构,就会在这里发生死循环,造成悲剧。











